Force is a core principle in physics that we experience in our daily lives frequently without conscious awareness. In essence, force refers to a push or pull that can initiate movement, halt an object, or alter its trajectory. Grasping the concept of force enhances our understanding of the natural environment and the various interactions that take place within it. This article will delve into the definition of force, its different types, and its significant impact on our everyday experiences.
What is Force?
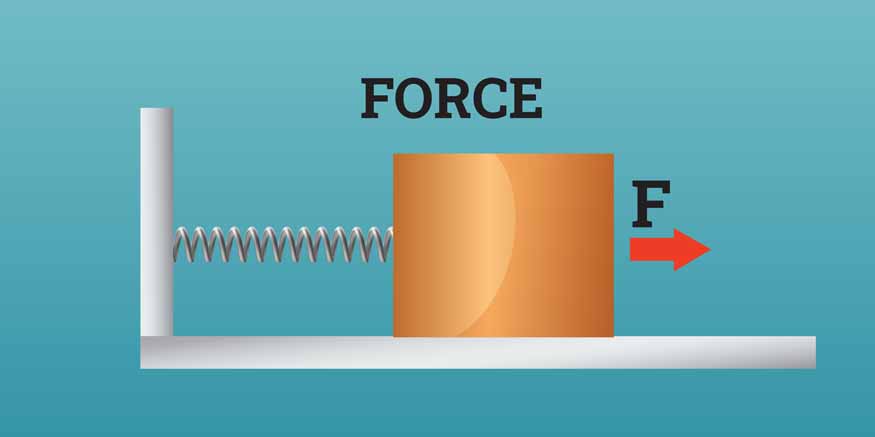
In the field of physics, force is an interaction that changes the motion of an object. It is a vector quantity, that possesses both magnitude and direction. The standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) is the Newton (N), a designation that honours Sir Isaac Newton, the pioneer of the laws of motion.
According to Newton’s First Law of Motion, often referred to as the law of inertia, an object at rest will remain at rest. On the other hand, an object in motion will persist in its motion at a constant velocity unless influenced by an external force.
This concept highlights the force’s critical role in modifying the motion state of objects.
Types of Forces
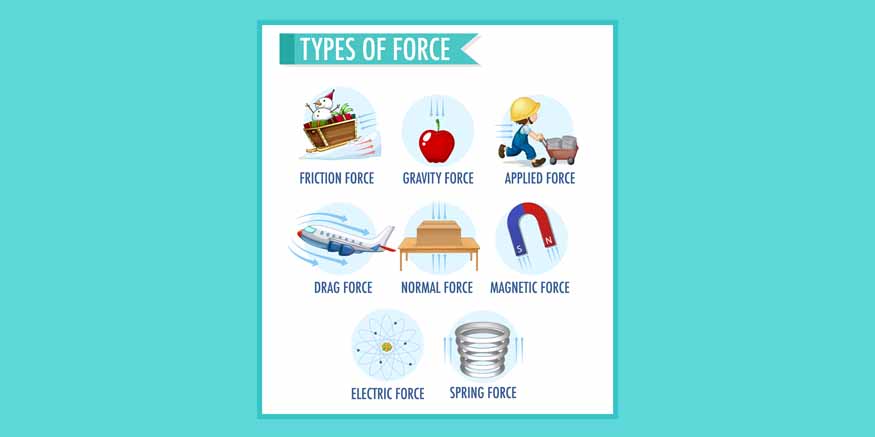
There are various types of force that we experience in our everyday lives. The primary types include:

Gravitational Force: This force is the attraction between two masses. It explains why objects fall to the ground and why celestial bodies, such as planets, revolve around the sun. On Earth, gravity provides weight and keeps us grounded.
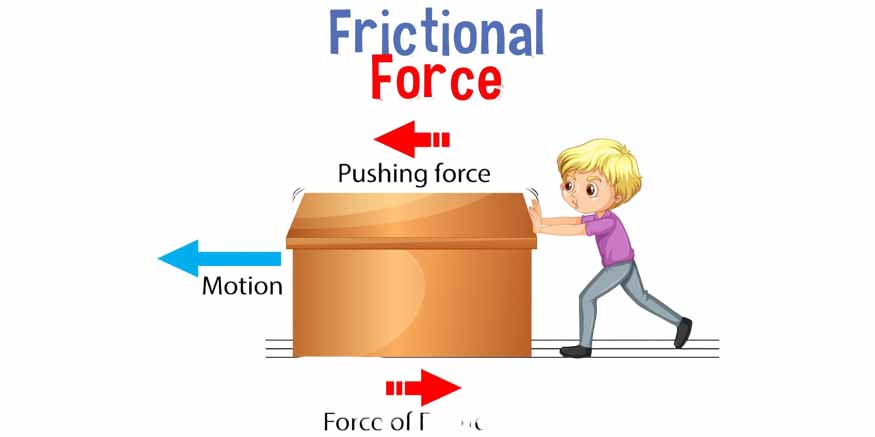
Frictional Force: Friction opposes the movement of an object and occurs between surfaces in contact. It enables us to walk without slipping and allows vehicles to halt when brakes are applied.
Normal Force: When an object is placed on a surface, an upward force is exerted by the surface known as Normal Force . This force counteracts the object’s weight, preventing it from falling through the surface.
Tension Force: A force that is transmitted through a string, rope, or wire when it is pulled tight by opposing forces is referred as Tension. It is responsible for keeping a rope tight when both ends are pulled.
Applied Force: This force is exerted on an object by a person or another object. For instance, when you push a door open, a force is being applied on it called Applied Force.
Air Resistance Force: This is a type of frictional force that acts on objects as they travel through the air. It is the reason parachutes decelerate when deployed. This force is commonly referred as ‘drag’.
Force in Everyday Life
Force is an essential element in our everyday activities that often impacts our actions in many ways. Here are several instances illustrating the impact of force in our daily lives:
Walking and Running: As we walk or run, our feet exerts a force against the ground, pushing us forward. This process involves both the applied force and frictional force. The friction between our feet and the surface helps prevent slipping, while the force we generate facilitates our movement.
Driving a Car: The engine produces an applied force that drives the car forward. The friction between the tyres and the road is crucial for acceleration, deceleration, and turning the vehicle. Additionally, air resistance opposes the vehicle’s motion, influencing fuel efficiency.
Using Tools: Tools like hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches enable us to apply force effectively. For instance, when you hammer a nail a force is exerted on the nail driving it into the wood. Similarly, using a wrench involves applying torque, or rotational force, to tighten or loosen bolts.
Lifting Objects: Lifting an object requires a force greater than gravity. Your muscles generate a force that exceeds the gravitational pull on the object, enabling you to lift it successfully.
Playing Sports: Sports encompass a variety of forces from kicking a soccer ball to throwing a javelin rod by applying a force that moves the objects forward. The ball’s path will be influenced by gravitation while friction force between the ball and the ground will slow it down.
Using Electronic Devices: Many electronic devices, including smartphones and laptops, feature touchscreens. When you tap or swipe on the screen, you apply a small force and that the device responds to the action by recognising it.
Weather Phenomena: Forces also play a significant role in weather systems. Air moving from areas of high pressure to low pressure cause ‘Wind’, driven by pressure differences. Gravity influences precipitation, causing rain to fall to the earth.
Interesting Fact: Universal Gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object.
Conclusion
Force is a fundamental concept that influences almost every aspect of our lives. From the simple act of walking to the complexities of weather systems, forces shape our world and dictate how objects interact. By understanding the different types of force and their roles, we gain a deeper insight into the natural phenomena around us. Whether lifting a book, driving a car, or playing a sport, the principles of force are at work make everyday activities understandable.
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.